Table of Contents
telomere-targeted therapy Lung cancer is a devastating disease that claims millions of lives each year. Despite advances in medical science, treatment options for lung cancer remain limited, especially in cases where the disease has progressed to advanced stages. However, researchers are constantly seeking innovative approaches to combat this deadly form of cancer. One such avenue of exploration involves targeting telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, which play a crucial role in the development and progression of cancer.
Understanding Lung Cancer and telomere-targeted therapy
Lung cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lungs. It is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer worldwide, with smoking being the leading cause in many cases. Lung cancer poses significant challenges due to its aggressive nature, limited treatment options, and a high mortality rate. Conventional treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, often have limited efficacy in advanced cases. Therefore, there is a critical need for novel therapeutic strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Telomeres and Their Role in Cancer Development
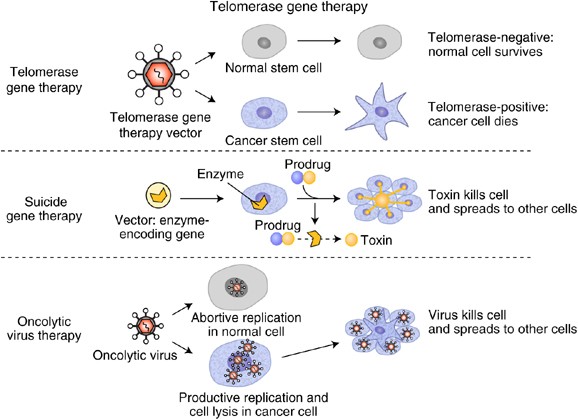
Telomeres are protective structures consisting of repetitive DNA sequences and proteins that cap the ends of chromosomes, safeguarding them from degradation and fusion. They play a vital role in maintaining genomic stability and regulating cellular aging. Telomeres naturally shorten with each cell division until they reach a critically short length, triggering cellular senescence or programmed cell death. In cancer cells, the enzyme telomerase becomes reactivated, allowing the lengthening of telomeres, which enables the unlimited proliferation characteristic of cancer.
The Potential of Telomere Targeting in Lung Cancer Treatment
Researchers have been exploring the potential of targeting telomeres as a therapeutic strategy for various types of cancer, including lung cancer. One approach involves inhibiting the activity of telomerase, effectively limiting the ability of cancer cells to maintain their telomeres and replicate indefinitely. Several telomerase inhibitors have shown promising results in preclinical studies, inhibiting cancer cell growth and inducing cell death.
Additionally, alternative telomere-targeting approaches are being investigated. These include disrupting the shelterin complex, which protects telomeres, or using small molecules that specifically target telomere DNA. By interfering with telomere maintenance mechanisms, these strategies aim to impair the viability of cancer cells while sparing normal cells.
Current Research on Telomere Targeting for Lung Cancer
The potential of telomere targeting in lung cancer treatment has garnered significant attention from the scientific community. Preclinical studies utilizing telomerase inhibitors and alternative telomere-targeting approaches have demonstrated promising results in inhibiting lung cancer cell growth and inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death). These findings have provided a strong foundation for further investigation in clinical settings.
Clinical trials evaluating telomere-targeted therapies are underway, assessing their safety, efficacy, and potential side effects. Initial results from these trials have been encouraging, demonstrating the feasibility and potential benefits of telomere targeting in lung cancer treatment. However, further research and larger-scale trials are needed to establish the long-term efficacy and safety profiles of these treatments.
Promising Outcomes and Challenges in Telomere-Targeted Therapy
Telomere-targeted therapy offers several potential advantages for lung cancer treatment. By selectively targeting cancer cells while sparing normal cells, these therapies may minimize adverse effects associated with conventional treatments. Moreover, telomere-targeted approaches have the potential to overcome resistance mechanisms developed by cancer cells, making them a promising avenue for combating drug-resistant lung cancers.
However, challenges remain in the development and implementation of telomere-targeted therapies. Ensuring the specificity and efficacy of these treatments while minimizing off-target effects is a complex task. Additionally, strategies to overcome potential resistance to telomere-targeted therapies need to be explored. Further research is also necessary to optimize the delivery methods of these treatments and identify biomarkers that can predict patient response and guide treatment decisions.
The Future of Telomere-Targeted Treatments for Lung Cancer
Despite the challenges, the exploration of telomere-targeted treatments for lung cancer holds immense potential. As research progresses and more data becomes available, these therapies may become an integral part of the lung cancer treatment landscape. They have the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes and offer new hope to those affected by this devastating disease.
The continued collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies is essential to further advance telomere-targeted therapies. By addressing the remaining challenges and refining treatment strategies, the future looks promising for this innovative approach in lung cancer treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, researchers are actively investigating the potential of targeting telomeres as a novel therapeutic strategy for lung cancer. Telomere-targeted treatments, including telomerase inhibitors and alternative approaches, have shown promising results in inhibiting cancer cell growth and inducing apoptosis in preclinical studies. Clinical trials are underway to assess the safety and efficacy of these therapies in lung cancer patients. While challenges remain, the future of telomere-targeted treatments for lung cancer appears promising, offering new possibilities for improved patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are telomeres only relevant to lung cancer? No, telomeres play a role in various types of cancer and are being studied as potential targets in multiple cancer types, including lung cancer.
2. How do telomerase inhibitors work? Telomerase inhibitors block the activity of the telomerase enzyme, which is responsible for maintaining telomere length in cancer cells. By inhibiting telomerase, these inhibitors limit the ability of cancer cells to divide and replicate.
3. What are the challenges in developing telomere-targeted therapies? Developing telomere-targeted therapies requires addressing challenges related to specificity, efficacy, off-target effects, and potential resistance mechanisms. Delivery methods and the identification of predictive biomarkers are also areas of focus for further research.
4. Can telomere-targeted therapies be used alongside other treatments? Combining telomere-targeted therapies with other treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy, is an area of active investigation. Combination approaches have the potential to enhance treatment efficacy and overcome resistance.
5. How can I learn more about telomere-targeted treatments for lung cancer? For more information on telomere-targeted treatments and the latest advancements in lung cancer research, consult with your healthcare provider or refer to reputable scientific publications and websites focused on cancer research and treatment